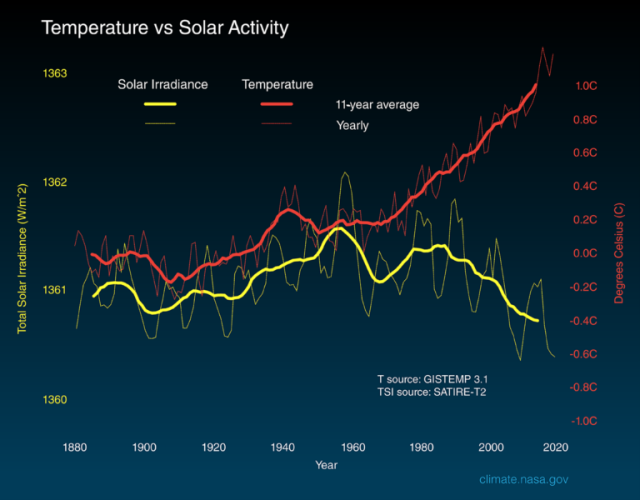
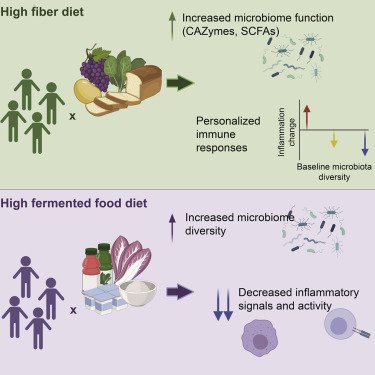
As climate change continues to exacerbate the challenges posed by rising global temperatures, the world is facing a growing threat to food security. The consequences of this crisis are far-reaching and multifaceted, with devastating impacts on farmers, communities, and ecosystems worldwide.
One of the most pressing concerns is the disruption to agricultural production systems. Warmer temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are all taking their toll on crops and livestock, leading to reduced yields, lower quality produce, and decreased food availability. This can have severe consequences for people who rely on these staple foods for sustenance.
The effects of climate change on food security are particularly pronounced in vulnerable communities, where limited access to resources, infrastructure, and economic resilience make it even more difficult to adapt to the changing climate. From drought-stricken farmlands to flooded coastal areas, the impacts of climate-related disasters can be catastrophic, pushing millions of people into food insecurity and poverty.
However, despite these daunting challenges, there are many innovative strategies being employed to ensure that everyone has access to nutritious food. One approach is through the development of climate-resilient agriculture (CRA) systems, which prioritize sustainable farming practices, agroforestry, and conservation agriculture. By adopting these methods, farmers can improve soil health, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and enhance crop yields in the face of climate change.
Another key strategy is the use of technology to support smallholder farmers and vulnerable communities. From precision irrigation systems to mobile apps for crop monitoring and market access, cutting-edge innovations are being harnessed to bridge the gap between producers, consumers, and markets. By leveraging digital platforms, social media, and mobile payments, these initiatives can help build more resilient food systems, improve income opportunities, and enhance food security.
Furthermore, policymakers and international organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of addressing climate change through agricultural development. Initiatives such as sustainable agriculture loans, crop insurance schemes, and climate-resilient infrastructure investments are being implemented to support farmers in their efforts to adapt to changing climatic conditions.
Finally, there is a growing recognition that food security is not just about individual households or communities but also about the broader social fabric of society. Efforts to promote social cohesion, address hunger, and ensure nutrition equity are gaining momentum as governments, civil society, and private sector actors come together to forge more inclusive and resilient food systems.
In conclusion, while climate change poses significant challenges to global food security, there is growing recognition that these can be overcome through innovative strategies and collaborative efforts. By prioritizing sustainable agriculture practices, leveraging technology, supporting smallholder farmers, and fostering social cohesion, we can build a more resilient food system that provides nutritious food for all, regardless of where they live or how much they earn.