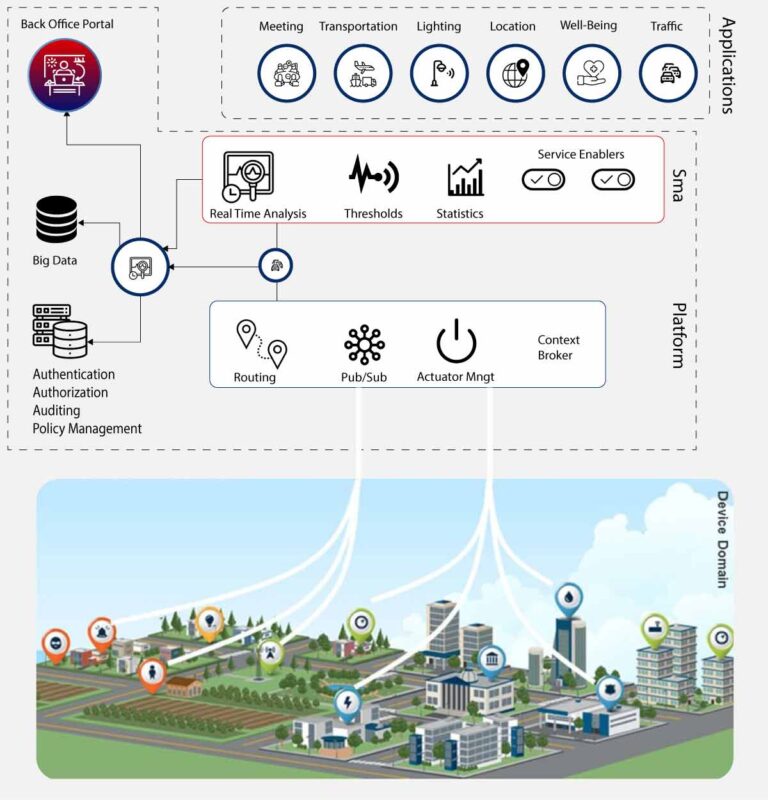
Despite the widespread adoption and growing investment in 5G technology, many experts argue that the network is still far from being fully realized. Recent studies have shed light on several key areas where 5G networks continue to lag behind expectations, casting doubt on their readiness for mainstream use.
One of the most significant challenges facing 5G is its capacity to deliver reliable and consistent connectivity in dense urban environments. While initial tests have shown promising results, real-world trials have revealed a number of issues with congestion, dropped calls, and slow speeds. As cities continue to grow and become increasingly crowded, these problems are likely to worsen, making it difficult for 5G networks to meet the demands of heavy users.
Another area where 5G is falling short is in its ability to provide seamless handovers between different cells and networks. This is a critical function that enables smooth user experience, particularly for mobile operators who rely on this feature to provide high-quality service to their customers. However, tests have shown that 5G networks often struggle to maintain reliable handovers, leading to dropped calls, slow speeds, and other disruptions.
The lack of standardization in 5G technology is also a major concern. With different manufacturers and network operators developing their own unique features and protocols, it’s becoming increasingly difficult for devices and equipment to communicate effectively with each other. This can lead to compatibility issues, increased costs, and reduced performance, making it harder for users to get the best out of their 5G services.
In addition to these technical challenges, there are also concerns about the environmental impact of 5G networks. The increased demand for energy and data transmission is expected to result in significant increases in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly if not managed sustainably. As consumers become increasingly aware of the importance of reducing their carbon footprint, it’s essential that network operators prioritize sustainability and develop more environmentally friendly technologies.
Finally, there are also questions being raised about the economic viability of 5G networks. While initial investments have been significant, many experts argue that the revenue streams generated by these networks will not be enough to justify the costs of building out new infrastructure. This could lead to a situation where network operators struggle to maintain profitability, making it difficult for them to continue investing in research and development.
As 5G technology continues to evolve and mature, these challenges need to be addressed if the network is to reach its full potential. By tackling these issues and prioritizing innovation, reliability, sustainability, and economic viability, we can ensure that 5G networks deliver on their promises and provide a fast, reliable, and secure mobile experience for users worldwide.