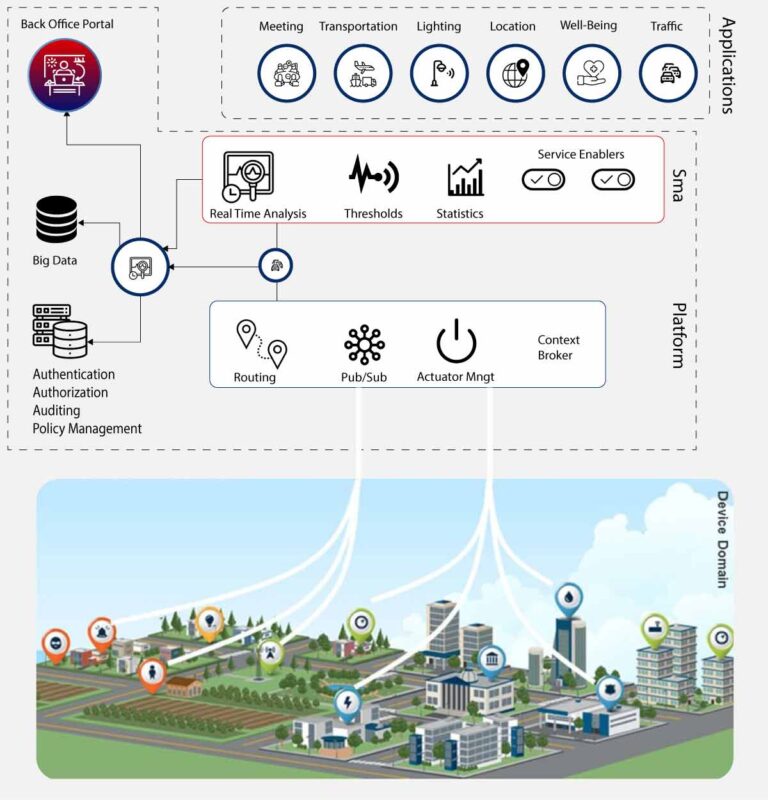
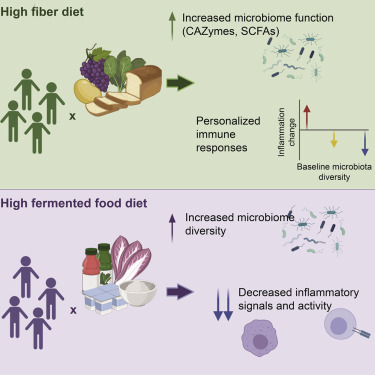
The Rise of Social Media and its Toll on Mental Health: A Growing Concern Among Young People
In recent years, social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of people around the world using platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter to connect with others, share their experiences, and stay informed. However, a growing body of research suggests that social media use can have a negative impact on mental health, particularly among young people.
Studies have shown that excessive social media use is linked to increased symptoms of anxiety and depression, as well as decreased self-esteem and life satisfaction. One study published in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence found that teenagers who spent more time on social media were more likely to experience depressive symptoms, including feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed.
Another study published in the journal Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking found that young adults who used social media more frequently were more likely to experience anxiety and stress, as well as decreased sleep quality and increased feelings of loneliness. The researchers suggested that this may be due to the constant stream of curated and manipulated content on social media, which can create unrealistic expectations and promote feelings of inadequacy.
The effects of social media on mental health are particularly concerning among young people, who are already vulnerable to the pressures of adolescence. A study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health found that teenagers who used social media more frequently were more likely to experience bullying, cyberbullying, and online harassment, which can have serious negative consequences for their mental health.
So, what can be done to mitigate the negative effects of social media on mental health? Some researchers suggest that parents, educators, and policymakers need to take a proactive approach to teaching young people about the risks and benefits of social media use. This could involve education programs that teach critical thinking skills, online safety, and healthy social media habits.
Others recommend that social media companies take steps to promote healthier usage patterns among their users. This could include features such as time limits, notifications filters, and algorithms that prioritize content from trusted sources over sensational or inflammatory material.
Ultimately, the relationship between social media use and mental health is complex and multifaceted, and more research is needed to fully understand its effects. However, by acknowledging the potential risks and taking steps to mitigate them, we can work towards creating a healthier digital landscape for young people.