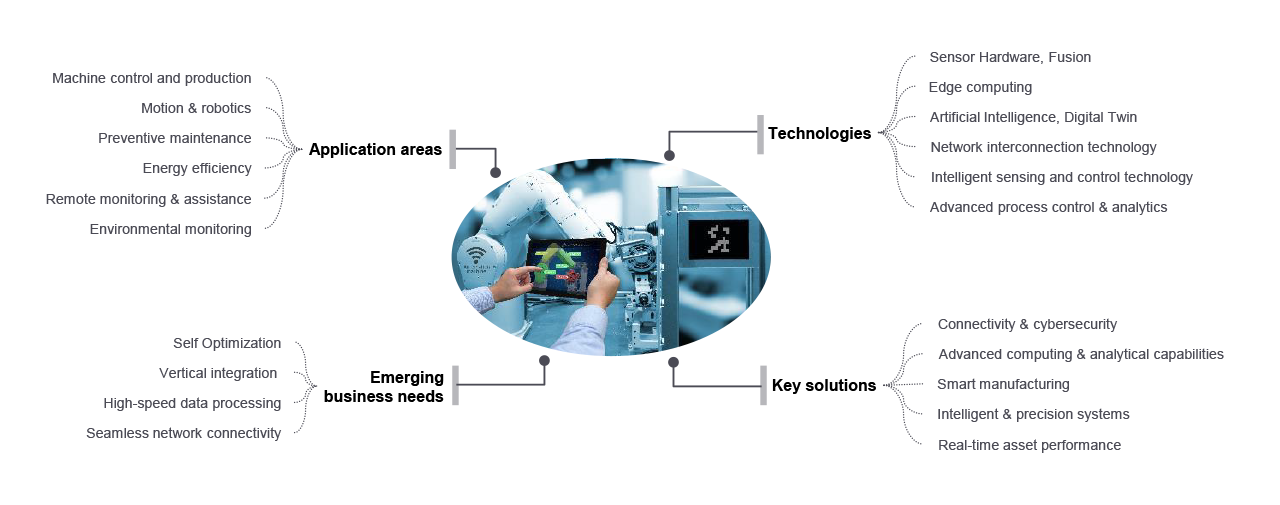
As the world grapples with the challenges of increasing production efficiency, reduced labor costs, and enhanced product quality, robotics technology has emerged as a game-changer in the manufacturing sector. The integration of robots in industrial settings has been on the rise, transforming the way goods are produced, packaged, and delivered to customers.
One of the most significant benefits of using robots in industry is their ability to perform repetitive and labor-intensive tasks with precision and accuracy. By automating these processes, manufacturers can reduce the risk of human error, increase productivity, and free up staff to focus on higher-value tasks that require creativity, problem-solving, and strategic thinking.
Another advantage of robotics technology is its ability to improve product quality and consistency. Robots equipped with advanced sensors and vision systems can inspect products during production, detecting defects or irregularities that might otherwise go unnoticed by human inspectors. This not only ensures higher-quality products but also reduces waste and minimizes the risk of costly rework.
Moreover, robots can be programmed to work in a variety of environments and under different conditions, making them an ideal solution for manufacturing operations that take place in remote or hard-to-reach locations. Additionally, their ability to operate 24/7 without fatigue or breaks means they can work around the clock, providing manufacturers with greater flexibility and control over production schedules.
However, the integration of robots into existing workflows also raises important questions about job displacement, worker safety, and the potential for technological errors. As automation increases, there is a risk that jobs may be lost to machines, particularly in sectors where tasks are highly repetitive or routine. Furthermore, the use of robots requires significant investments in training and maintenance, which can add complexity and costs to manufacturing operations.
Furthermore, researchers have identified various risks associated with robotics technology, including cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and potential liabilities arising from product malfunctions. To mitigate these risks, manufacturers must prioritize robust security measures, regular software updates, and effective testing protocols for their robotic systems.
As the adoption of robots in industry continues to grow, it is crucial that manufacturers develop strategies for integrating these technologies seamlessly into existing workflows. This might involve retraining staff to work alongside robots, upgrading infrastructure to accommodate new equipment, or exploring innovative solutions for data management and analytics. By harnessing the power of robotics technology and addressing its associated challenges, manufacturers can unlock unprecedented opportunities for growth, efficiency, and innovation.
Ultimately, the integration of robots in manufacturing will require a collaborative approach between industry leaders, policymakers, and technology developers. As we move forward into an increasingly automated future, it is essential that we prioritize worker safety, digital literacy, and responsible innovation to ensure that robotics technology benefits both people and the planet as a whole.