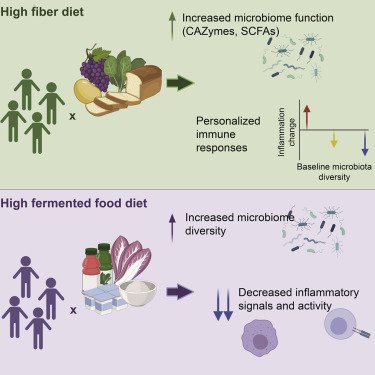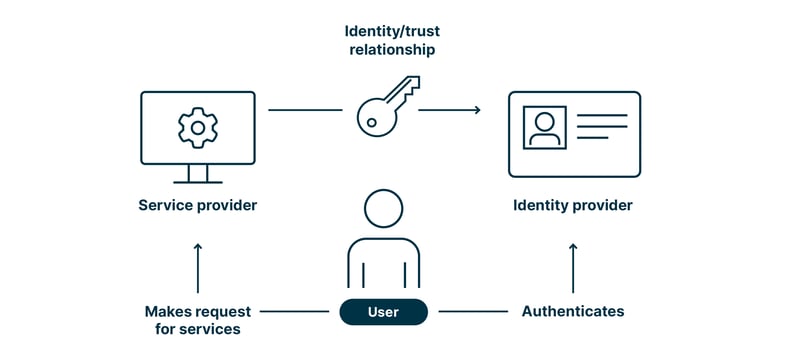
In recent years, the concept of decentralized identity management has gained significant attention as a means to enhance individual autonomy and control over personal data. One innovative approach that has emerged is the application of Blockchain technology in identity verification. By leveraging the immutable and transparent nature of blockchain, this method offers several benefits over traditional identity verification methods.
One of the primary advantages of using blockchain for identity verification is its ability to ensure the integrity and authenticity of an individual’s identity. Unlike centralized systems that rely on third-party verification processes, blockchain-based systems utilize a decentralized network of nodes to validate and verify identity claims. This reduces the risk of identity theft and tampering, as any attempt to manipulate or alter personal data would require significant computational resources and would be visible to all parties on the network.
Another benefit of using blockchain in identity verification is its potential to increase transparency and accountability. With a blockchain-based system, individuals can have control over their own identity data, ensuring that it is accurate and up-to-date. Additionally, the use of smart contracts can automate the verification process, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of bias or corruption.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain technology allows for greater mobility and flexibility in identity management. Individuals can move freely between countries or jurisdictions without worrying about having to re-verifying their identity each time they travel or apply for a new service. This can be particularly beneficial for refugees, migrants, and other vulnerable populations who often face significant barriers when trying to access basic services.
To implement blockchain-based identity verification systems, several key components are necessary:
1. Identity data storage: A secure and decentralized storage solution is required to store individual identity data, such as biometric information or personal documents.
2. Blockchain network: A decentralized network of nodes must be established to validate and verify identity claims.
3. Smart contracts: Automated rules and agreements can be programmed into smart contracts to govern the verification process and ensure that it is fair and transparent.
Several countries and organizations are already exploring the potential of blockchain-based identity verification systems, including Estonia, Japan, and the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR). While there are still significant challenges to overcome, the benefits of using blockchain in identity verification make it an exciting and promising area of development.