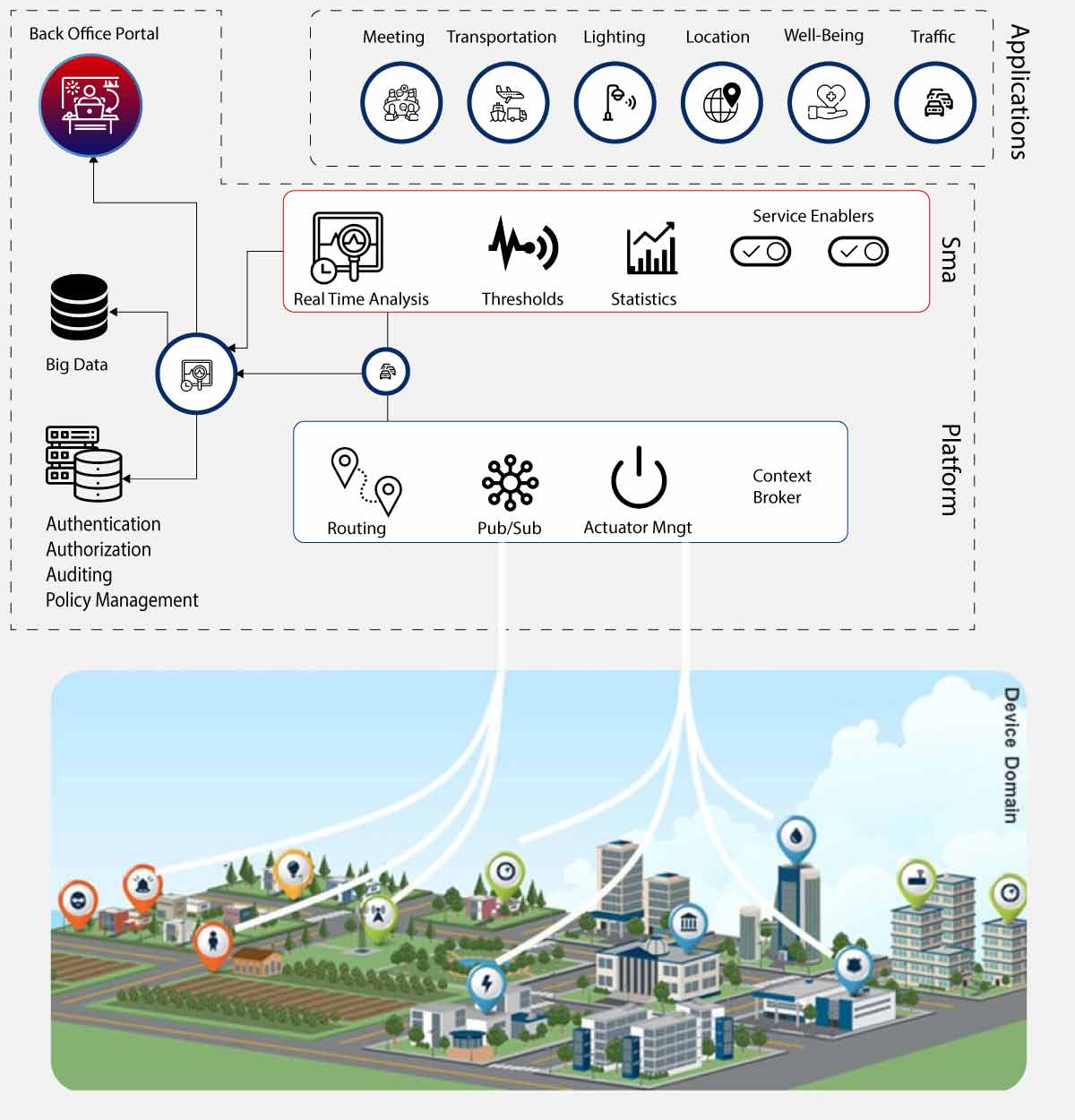
As cities continue to grow and evolve, the demand for efficient, sustainable, and livable spaces has never been more pressing. One key strategy that many urban planners are turning to is the integration of Smart City technology into their urban planning frameworks. At the heart of this movement is the Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure, a network of interconnected sensors, devices, and systems that collect and exchange data in real-time.
But why do cities need IoT infrastructure in the first place? The answer lies in its ability to provide a range of benefits that can have a profound impact on urban life. For instance, by monitoring traffic patterns and congestion, cities can optimize traffic flow, reducing travel times and decreasing air pollution. This, in turn, can lead to improved air quality, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and enhanced overall quality of life for residents.
IoT infrastructure also enables cities to manage waste management more effectively. By deploying sensors to track waste collection routes, volumes, and composition, cities can identify areas where waste reduction strategies can be implemented most effectively. This not only reduces the environmental impact of waste disposal but also helps to minimize costs associated with waste collection and disposal.
Furthermore, IoT infrastructure provides a platform for cities to offer smart services that enhance resident engagement and convenience. For example, by deploying sensors to monitor temperature and humidity levels in public spaces, cities can create comfortable environments for residents, especially during extreme weather conditions. This can lead to improved mental health and well-being outcomes, as well as reduced healthcare costs.
Another significant benefit of IoT infrastructure is its ability to support urban resilience. By providing real-time data on environmental conditions such as water pressure, storm surges, and seismic activity, cities can develop more effective disaster response plans and minimize the impact of natural disasters on residents.
In addition, IoT infrastructure provides a platform for cities to analyze and optimize energy consumption patterns. By deploying sensors to monitor energy usage in buildings and public spaces, cities can identify areas where energy efficiency improvements can be made, leading to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and cost savings.
Lastly, IoT infrastructure enables cities to create data-driven decision-making processes that inform policy development and resource allocation. By analyzing data from various sources, including sensors, social media, and mobile apps, cities can gain insights into resident behavior, preferences, and needs, ultimately leading to more effective urban planning strategies.
In conclusion, the integration of IoT infrastructure into urban planning frameworks is a critical component of Smart City technology. By providing real-time data on various aspects of city life, IoT infrastructure enables cities to optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, enhance resident engagement, support urban resilience, and create more sustainable environments. As cities continue to grow and evolve, it is essential that they prioritize the development of robust IoT infrastructure to ensure a brighter, more livable future for their residents.