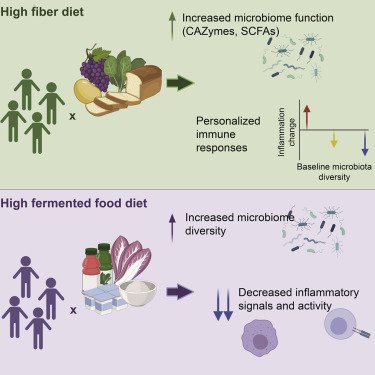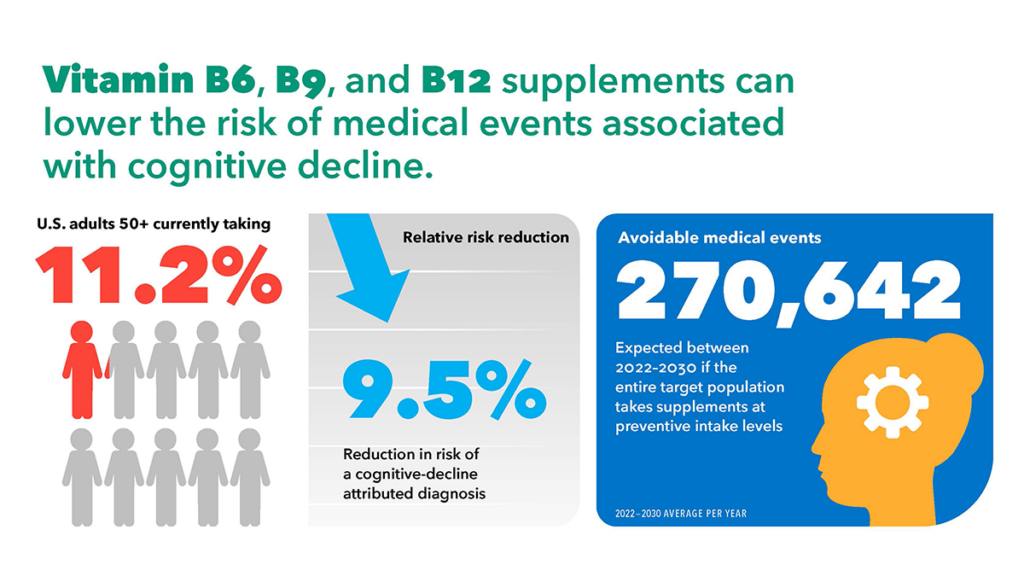
The Rise of Social Media: A Silent Threat to Cognitive Function
In today’s digital age, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. We spend hours scrolling through our feeds, sharing updates with friends and family, and staying connected with the world at large. While social media can be a powerful tool for social interaction and information dissemination, recent research published in the Journal of Behavioral Addictions suggests that excessive use may have a profound impact on our cognitive abilities.
Studies have consistently shown that prolonged exposure to social media is linked to a decline in attention span and memory. This phenomenon is often referred to as “continuous partial attention,” where individuals are constantly switching between multiple sources of information, leading to a decrease in focus and concentration. As a result, our ability to process and retain information becomes increasingly impaired.
One possible explanation for this effect is the way in which social media platforms are designed to activate the brain’s reward system. Social media algorithms use psychological manipulation techniques, such as likes, shares, and comments, to keep users engaged and coming back for more. This can lead to a vicious cycle of addiction, where individuals find themselves constantly checking their phones and scrolling through feeds in an effort to feel connected and validated.
But the consequences of this addiction go beyond mere entertainment. Excessive social media use has been linked to decreased cognitive performance, particularly in areas such as attention, memory, and problem-solving. This is likely due to the fact that our brains are not designed for constant multitasking or rapid-fire information processing. As we continue to spend more time staring at screens, our ability to focus and process information becomes increasingly impaired.
The implications of this research are far-reaching and have significant implications for individuals, families, and society as a whole. As social media use continues to rise, it is essential that we take steps to mitigate the negative effects on cognitive function. This may involve setting limits on screen time, practicing mindfulness and self-regulation techniques, and seeking out alternative forms of social interaction and entertainment.
Ultimately, the relationship between social media and cognitive decline highlights the need for a more nuanced understanding of the impact of technology on our lives. By acknowledging both the benefits and drawbacks of social media, we can work towards creating a healthier digital landscape that supports both individual well-being and societal progress.