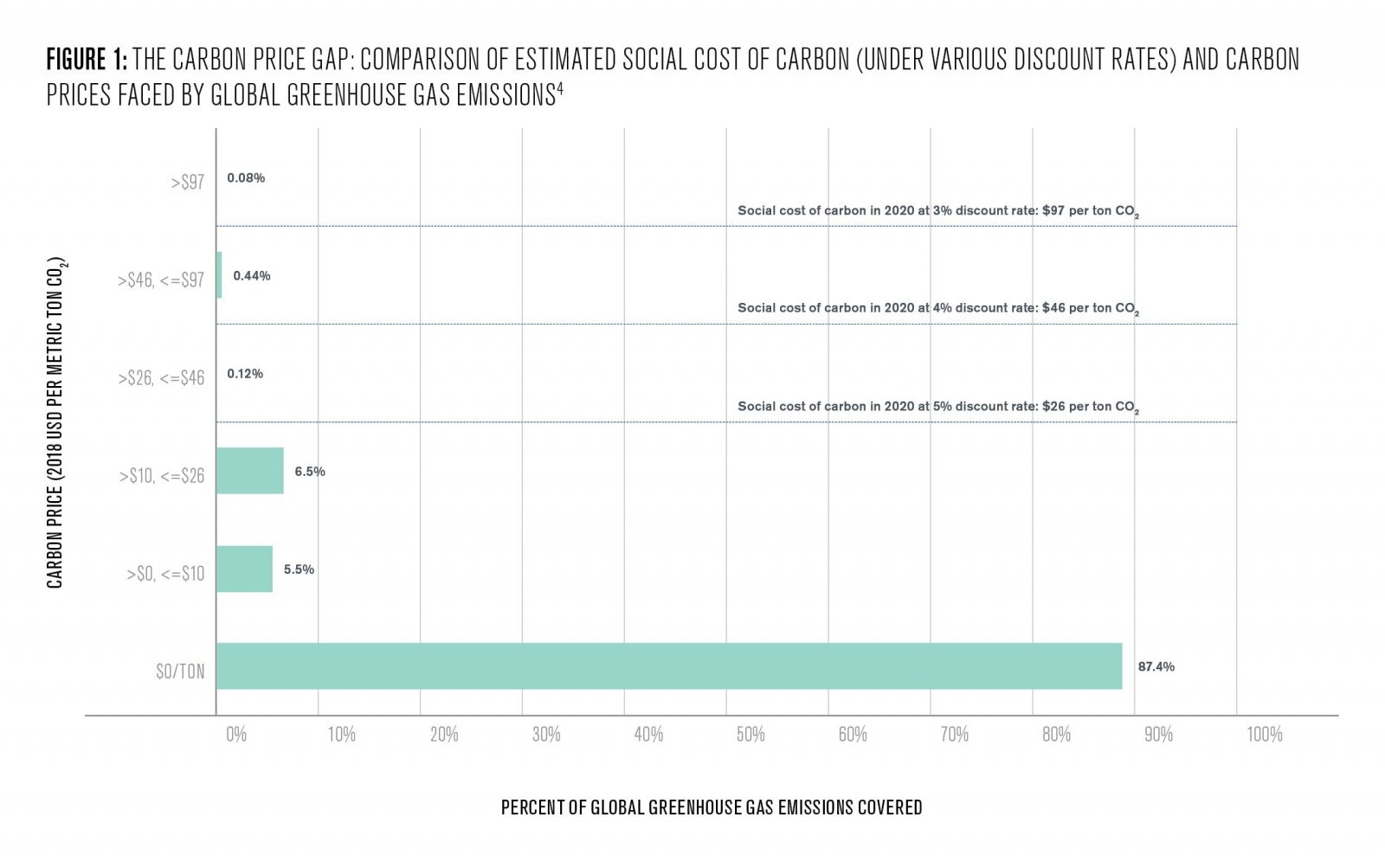
The concept of carbon pricing has gained significant attention in recent years as a crucial policy tool for mitigating climate change. By placing a financial value on carbon emissions, governments and businesses can create an economic incentive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition towards cleaner energy sources.
One of the primary benefits of carbon pricing is its ability to provide a clear economic signal to industries and individuals to adopt more sustainable practices. As the price of carbon rises, companies are incentivized to invest in low-carbon technologies and processes that reduce their carbon footprint. This not only helps to decrease emissions but also creates new business opportunities and jobs in the clean energy sector.
Carbon pricing can also serve as a level playing field for countries and businesses, promoting fair competition and innovation. Unlike other environmental regulations that can impose significant costs on certain industries, carbon pricing ensures that all players are held accountable for their emissions, regardless of their size or location. This fosters a more level playing field, encouraging companies to invest in low-carbon technologies and reducing the likelihood of carbon leakage.
Another key benefit of carbon pricing is its potential to generate revenue for governments to fund climate change mitigation efforts. By creating a financial instrument that rewards reductions in emissions, governments can raise significant funds to support clean energy projects, research and development, and other climate-related initiatives. This revenue stream can also help to offset the costs associated with implementing and enforcing carbon pricing policies.
Despite its benefits, carbon pricing has faced opposition from some quarters, primarily due to concerns over its fairness and equity. Some argue that the tax will disproportionately affect low-income households and small businesses, which may struggle to absorb the increased costs. However, many countries have implemented carbon pricing systems that include mechanisms for exemptions or rebates to mitigate these effects.
To overcome these concerns, it is essential to design a well-structured carbon pricing system that takes into account the needs and circumstances of all stakeholders. This can be achieved by implementing a tiered pricing structure, where emissions rates decrease as the price increases. Additionally, governments can provide support for vulnerable populations through targeted benefits or subsidies.
In addition to its economic benefits, carbon pricing has also been shown to have significant environmental impacts. By creating an incentive to reduce emissions, carbon pricing can drive the adoption of cleaner energy sources and increase energy efficiency. This can help to decrease greenhouse gas emissions from various sectors, including transportation, industry, and buildings.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges posed by climate change, it is essential that we explore innovative policy solutions like carbon pricing. By designing a well-structured system that balances economic, social, and environmental considerations, governments can create a level playing field for low-carbon growth and development.