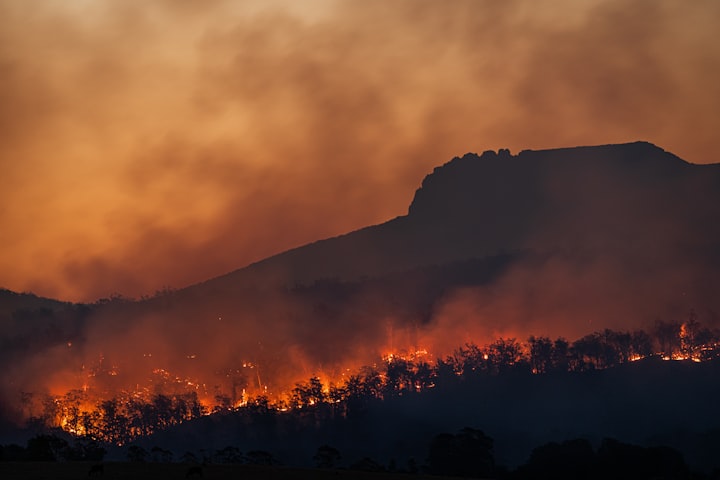
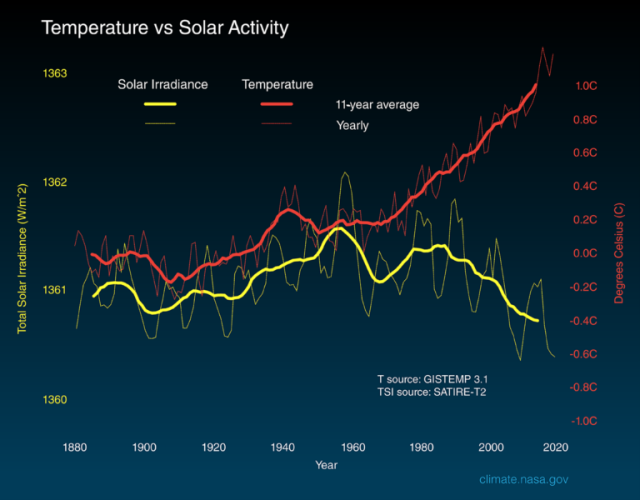
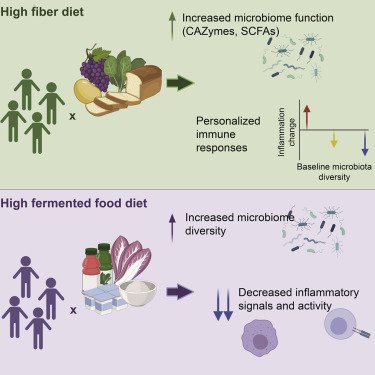
As climate change continues to affect global temperatures, biodiversity loss has become a pressing concern for humanity’s survival. The alarming rate at which species are vanishing from the face of the earth is not only a reflection of our planet’s fragility but also a warning sign that we must heed. With millions of plant and animal species facing extinction, it is imperative that we adopt effective strategies to protect and preserve our natural world.
One of the most critical approaches to addressing biodiversity loss is through the implementation of protected areas. National parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and other conservation reserves provide a safe haven for endangered species to thrive in an increasingly threatened environment. By safeguarding these habitats, governments and organizations can help maintain ecosystem balance and promote biodiversity hotspots.
Another key strategy being employed to combat biodiversity loss is rewilding. This concept involves reintroducing native species into areas that have been degraded or fragmented, allowing them to recolonize and restore ecological processes. Rewilding initiatives, such as the reintroduction of wolves in Yellowstone National Park, have proven successful in restoring ecosystem balance and promoting biodiversity.
In addition to protected areas and rewilding, there is a growing focus on sustainable land use practices. This includes agroforestry, permaculture, and regenerative agriculture – all of which aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining soil health and biodiversity. By adopting these methods, farmers and landowners can create more resilient ecosystems that are better equipped to withstand the impacts of climate change.
Community-based conservation initiatives also play a vital role in protecting biodiversity. Local communities, often the most knowledgeable about their ecosystem, can provide valuable insights into the needs and habits of native species. By empowering local populations to manage their own lands, governments and organizations can foster a sense of ownership and stewardship that drives long-term conservation efforts.
Furthermore, technological advancements are being harnessed to support biodiversity conservation. Advanced sensors, drones, and satellite imaging allow scientists to monitor ecosystem health in real-time, detect early signs of decline, and track the effectiveness of conservation strategies. These tools also enable researchers to study species migration patterns, habitat fragmentation, and the impacts of climate change on ecosystems.
As the world grapples with the challenges of biodiversity loss, it is clear that a multifaceted approach is needed. By combining protected areas, rewilding, sustainable land use practices, community-based conservation, and technological innovation, we can begin to reverse the alarming trends in species decline and restore the health and resilience of our planet’s ecosystems.